In March I had just returned from Philadelphia, where the 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-2025) took place from February 25th to March 4th. It was an incredibly intense week; while the city greeted us with a crisp chill, the atmosphere inside the convention center was electric, fueled by heated debates between researchers, practitioners, and engineers.
For me, this wasn’t merely a business trip, but a firsthand look at the trajectory of AI. This year’s program was massive in scope—ranging from the rigorous main technical track to vital initiatives like AI for Social Impact and the Bridge Program, the latter of which facilitates cross-disciplinary synergy to tackle complex global challenges. I was particularly impressed by the Doctoral Consortium, where I had the chance to engage with PhD students who are currently defining the next frontier of the industry.
Core Insights: Key Trends and Directions
After meticulously reviewing the proceedings and engaging in hallway discussions, I’ve identified six pivotal trends that are set to shape the AI landscape in the coming years:
- Autonomous Agents: This is arguably the most dominant trend. We are shifting from static chatbots toward sophisticated agents capable of modeling complex behaviors and making autonomous decisions.
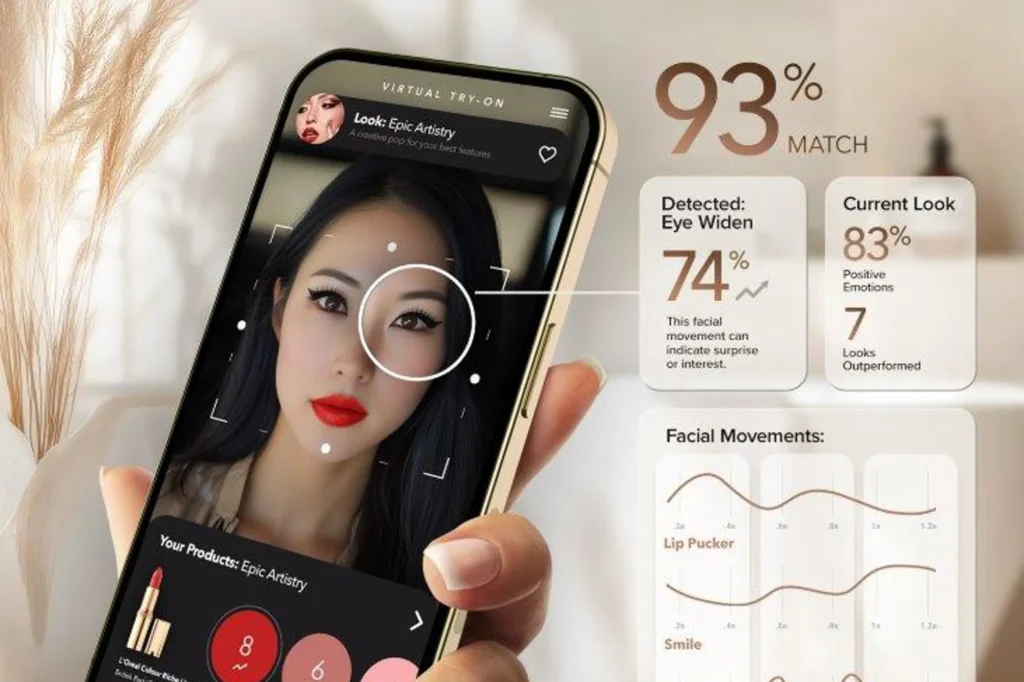
- Computer Vision: Vision systems are becoming increasingly nuanced. Notable highlights included I-FAS for facial recognition and the TC-LLaVA framework, which significantly advances our understanding of video dynamics.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Multimodality: The focus has shifted toward the integration of diverse data types. Key developments include the CoMT benchmark and CriSPO, a method for prompt optimization that enhances generative quality.
- Data Mining: The current frontier is the mitigation of noise in massive datasets. The RDGSL method for structure-aware representation learning in dynamic graphs looks particularly promising.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): There is a heavy emphasis on decision-making under uncertainty. A standout was the Selective Uncertainty Propagation method, which brings much-needed stability to offline RL.
- Machine Learning (ML): Applied tasks remain a priority. I was struck by the P-sLSTM algorithm for long-term time series forecasting and Attentive Eraser, which is currently the gold standard for object removal in diffusion models.
Deep Dive: When AI Enters the Political Arena
The highlight of the conference for me was a presentation by researchers from Wuhan University regarding the Political Actor Agent (PAA) framework. In essence, they have leveraged Large Language Models (LLMs) to simulate the intricacies of a legislative system.
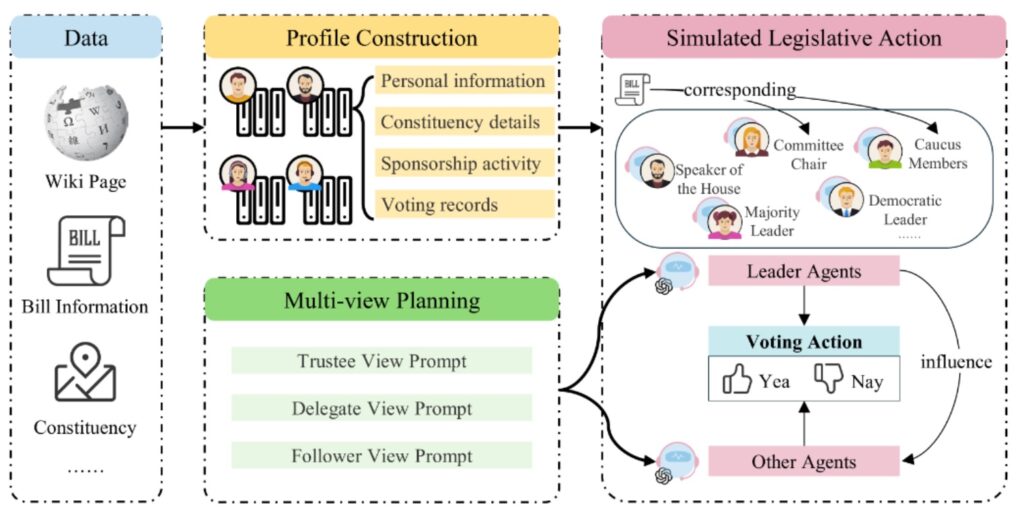
Why is this a breakthrough? Traditionally, predicting legislative roll-call votes has been notoriously difficult due to the volatility of human political behavior. PAA addresses this through a role-playing architecture where agents “embody” politicians to simulate the deliberation process. The authors validated the system using data from the 117th and 118th U.S. Congresses, and the results were remarkable.
What truly impressed me was the interpretability. The system doesn’t just provide a binary “yes/no” prediction; it offers a multi-faceted, human-readable rationale for each decision. This provides a transformative analytical tool for political science.
Philadelphia proved once again that a multidisciplinary approach is not just a buzzword—it is the only viable path to meaningful innovation. It was an exhilarating week, and these notes are just the beginning.
In my next post, I’ll dive deeper into other specific technologies showcased at AAAI-2025. Which of the trends mentioned above caught your attention the most?